Supply chain moves the world. Every time something is made, shipped, or delivered, there’s a whole web of suppliers, manufacturers, carriers, and buyers doing the heavy lifting behind the scenes. But often what holds things up isn’t the physical transportation, but finance and payments.
That’s where fintech in supply chain comes in, bringing speed, transparency, and flexibility to get goods moving and money flowing. If you’re in the logistics, procurement, or operations world, the shift is all around you.
Today, we’ll explore how fintech is transforming supply chain payments, supply chain finance, and embedded finance in transport and logistics. We’ll also dig into real benefits, challenges, and ecosystem opportunities so you can see why fintech is the next supply chain frontier.
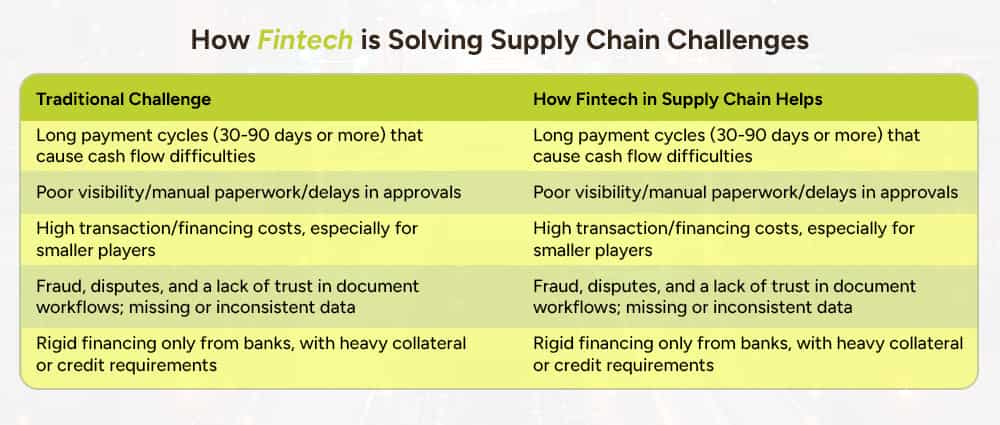
To understand why fintech is the next supply chain frontier, picture this: suppliers often wait 30, 60, sometimes 90 days to get paid after delivering goods. Carriers and logistics providers often face delayed invoices, confusing accessorial charges (think fuel surcharges, demurrage, etc.), and a lack of visibility when their payments will clear.
On the buyer side, companies want to hold onto cash as long as possible, but if payments are too slow upstream, that delays everything downstream.
That mismatch causes all kinds of friction:
Enter fintech: solutions that digitize, automate, finance, and embed payments and funding throughout the supply chain. When done right, Fintech’s Impact on Supply Chain Payments is massive.
Here are some of the main levers fintech is pulling in logistics and supply chain management:
Classic tools like reverse factoring or invoice financing, where suppliers can get early payment of invoices (at a discount), and buyers can extend payment terms without hurting supplier relationships. This helps both sides manage working capital better.
Moving from paper checks or manual bank transfers to electronic / API-based payments. Real-time or near-real-time payments reduce uncertainty and speed up the whole chain.
Embedding financing, payment, insurance, or credit options directly into the platforms that carriers, freight forwarders, or shippers use. For example, when a carrier completes a shipment, they can immediately get paid via a fintech service built into their dispatch or transport management software.
E-invoicing, digital dashboards, real-time tracking of payments and shipments, AI-based risk logistics scoring, blockchain or smart contracts to ensure documents and payments trigger only when certain conditions are met.
Let’s talk about the challenges with supply chain transactions and how fintech addresses them.
The embedded finance market was valued at US$82.7 billion in 2023, and it is forecast to reach US$570.9 billion by 2033, growing at about 21.3% CAGR.
In the logistics and wholesale trade sector, embedded finance is taking off: ~83% of PayFacs, ~80% of marketplaces and ~64% of ISVs express “strong interest” in digital wallets as part of embedded finance innovation.
These numbers show demand is high, and suppliers, carriers, and platforms see clear upside.
If you’re considering adopting fintech solutions, here are the concrete benefits that supply chains are getting:
Improved Working Capital & Liquidity: Suppliers get funds earlier; buyers can stretch out payables without hurting the supplier’s balance sheet. SCF helps optimize working capital.
Lower Cost of Financing: Because financing is often based on the creditworthiness of large buyers, or alternative risk assessments (via fintech tools), cost of capital for suppliers can be materially better than if they went to a traditional bank.
Faster, More Reliable Payments: Less lag from delivering goods to getting paid. Less uncertainty for carriers and smaller suppliers.
Greater Transparency & Visibility: Everyone in the chain can see where a payment or shipment is, what stage an invoice is at, what’s owed or due. That reduces disputes and improves trust.
Operational Efficiency & Cost Savings: Less manual work, less error, faster reconciliations. Platforms, APIs, and automated workflows reduce admin costs.
Better Relationships with Suppliers & Carriers: Suppliers like early payment options; businesses that offer embedded finance or supply chain finance tend to foster loyalty and stability in their logistics networks.
There’s a growing ecosystem of fintechs, platforms, carriers, software vendors, banks, and investors focused on supply chain fintech. Some opportunities in that ecosystem:
Putting this all together: fintech is not just a nice add-on. It’s becoming essential. Supply chains are more complex than ever, global shocks (pandemics, trade disruptions, fuel costs, geopolitical risk) show that any delay in financing or payment ripple quickly.
Fintech brings, which means it makes sure suppliers don’t go under because of delayed invoices; making sure carriers get paid so they don’t cut corners; making sure buyers can manage their cash sustainably without squeezing their network.
Also, customers (the end users) expect faster, more reliable last-mile delivery, lower costs, transparency. If logistics costs are high because of inefficiencies in payment or financing, that often trickles into end prices or delays. Fintech helps reduce those costs and delays.
So, for businesses that are still relying largely on manual, paper-based, or very traditional payment and financing systems, the risk is falling behind. Those embracing fintech will be more agile, more competitive, more trusted.
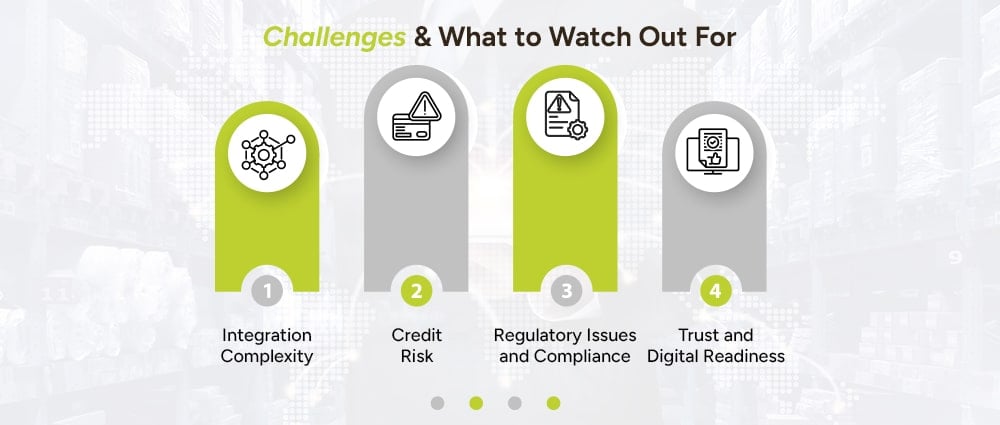
Of course, fintech doesn’t magically fix everything. Some of the challenges with supply chain transactions and supply chain fintech include:
Connecting Systems (ERP, shipping, invoicing) across buyers, suppliers, and logistics providers is not trivial.
For suppliers, even if the buyer is solid, finance providers need confidence; sometimes upstream suppliers further removed are harder to assess.
Cross-border payments, KYC/AML rules, data protection, financial regulations vary by region.
Cost of Adoption:
For smaller firms, platform fees, technology costs, training, may be barriers.
Some suppliers or carriers may distrust new platforms or don’t have reliable internet/data systems; paper, legacy systems are deeply entrenched.
In the next few years, expect:
At Arpatech, we help logistics and supply chain companies integrate Fintech-driven solutions, from automated payments and smart financing modules to AI-based analytics and embedded finance systems.
Whether you’re looking to streamline operations or build secure, scalable platforms, our custom software development services can help you stay ahead in the evolving Fintech landscape..
Traditional supply chain finance often struggles with:
One common example: imagine a large retailer buys from many suppliers, with payment terms of 60 days. A supplier delivers goods and issues an invoice. Rather than waiting for 60 days, the supplier has the option to use a supply chain finance platform, which pays them early (say day 5 or 10) at a small discount. Then the retailer still pays the financier on the 60th day.
So, the supplier gets cash early, the buyer maintains its cash for a longer period, and the financing provider earns a fee/discount. This helps suppliers smooth out cash flow, buyers manage working capital, and finance providers get a predictable business.
Supply chain finance is used by:
Global supply chains that include cross-border trade and many suppliers/carriers in different regions.
Technology companies/software vendors building tools to embed payments and finance within logistics, transport management, or procurement systems.