Healthcare has gone digital. Today’s patients want convenience, and healthcare providers want streamlined processes. That’s where patient portal software comes in.
Whether you’re a hospital admin or a health-tech startup founder, this guide breaks down everything you need to know about patient portal software development in 2025: from types and features to cost and compliance.
Patient portals: secure online accommodations for patients to access their medical records, communicate with providers, and manage their care at their convenience at any time of the night or day. These offer personalized and yet transparent healthcare experiences that can find an apt place in between patients and their healthcare providers.
Think of it like online banking, but for your health.
Thus, healthcare is moving at quite a pace, and patients expect more in controlling their health journeys. Patient portal software development thus helps them realize the above-mentioned goals through reduced paperwork, increased transparency, and the establishment of less time-consuming channels of communication.
It also enhances compliance, thus increasing patient satisfaction, which are the two primary objectives in modern healthcare.
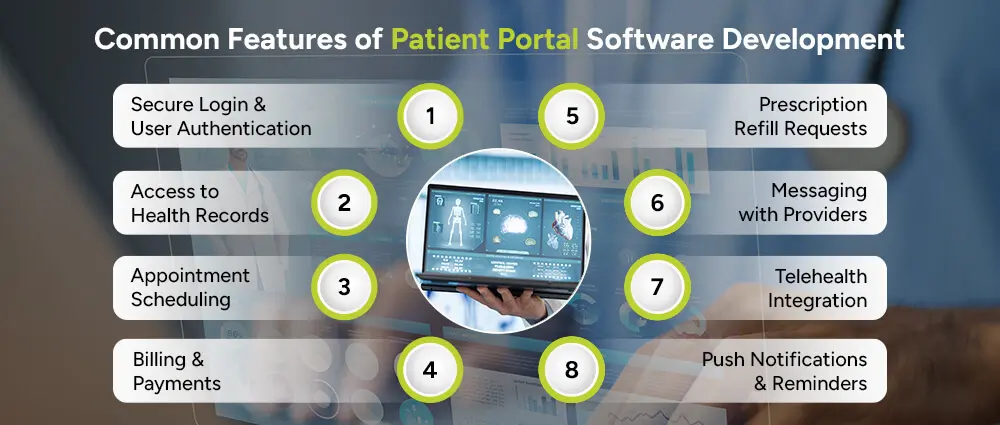
When you’re planning patient portal development for healthcare providers, these features are typically essential:
Patients must log in through a secure portal, often using two-factor authentication to ensure data is protected against unauthorized access.
Health access would allow patients to view their lab results, diagnoses, prescriptions, and past visit notes, putting them in charge of their health.
The patient can use the portal to book or reschedule appointments or cancel them without having to call up the clinic or wait in line.
Securely view medical bills, make payments online, and access insurance coverage information, all in one place.
Rather than calling a clinic, patients can request medication refills through the portal with just a few clicks.
Patients can send secure messages to their doctors, nurses, or administrative staff for non-emergency concerns and follow-ups.
The integration of telehealth services in the portal includes video consultations, which provide patients with easy access to care from home.
Patients receive automatic alerts reminding them of upcoming appointments, test results, and unread messages, thus keeping them in the know.
As patient expectations grow, modern patient portal app solutions are becoming more intelligent and personalized:
Integrated AI tools help patients identify possible conditions and guide them toward the right care without immediate doctor input.
Based on medical history and lifestyle data, the portal can deliver tailored health recommendations and reminders.
Sync with devices like smartwatches to track vitals such as heart rate, steps, or blood pressure in real-time.
Portals now offer interfaces in multiple languages to improve accessibility for diverse patient populations.
Features like screen readers, text enlargement, and voice navigation support patients with visual or physical disabilities.
Authorized caregivers or family members can manage medications, view test results, and book appointments for their loved ones.
The value of patient portal software lies in the variety of data it can handle, all from a single platform:
Patients can view their medical history, diagnoses, test results, and immunization records at any time.
Especially important for children, travel, and public health events, this data helps patients stay current on required vaccines.
Patients get notified and can review lab results as soon as they’re uploaded, often faster than waiting for a call.
After each appointment, patients receive a summary including physician notes, treatment plans, and prescribed medications.
Personalized care plans are accessible online, helping patients stay on track with medications, therapy, or follow-ups.
Complete lists of prescribed drugs with refill tracking help avoid medication errors and improve adherence.
Patients can check what their insurance covers, view balances, download invoices, and pay bills online.
Physicians can upload progress updates, allowing patients to track their recovery and understand next steps.
Depending on the healthcare setting, user requirements, and cloud software, different types of patient portal software can be developed:
These are developed as independent solutions and are often preferred by small practices that don’t have existing EHR systems.
These are connected to the provider’s existing Electronic Health Record system, creating a seamless data exchange between doctors and patients. This way, the providers can effortlessly provide healthcare IT support services in Dubai to doctors or patients if they find any glitch in the IT matrix.
Designed for smartphones and tablets, these apps give patients access on the go, perfect for busy individuals who need health data at their fingertips.
Built from the ground up, these are customized to the exact needs of a clinic, hospital, or health network, offering maximum flexibility and branding.
You’re probably wondering: how much does it cost to develop a patient portal? Here’s what to expect based on complexity:

Costs include design, development, testing, deployment, healthcare cloud migration, and post-launch support. A skilled custom patient portal development team can guide you in optimizing budget and features.
In 2025, patient portal software development is not just about digitizing medical records, it’s about empowering patients, improving outcomes, and making care more accessible for every person.
Whether you want to create a basic solution or a feature-rich platform, investing in a patient portal helps future-proof your healthcare delivery model. At Arpatech, our software development services are top-notch. Partner with our expert software and cloud experts and get future-ready patient portal today.
Typically, a basic version may take 3–4 months to put together. Highly customized and feature-rich portals may take 6–9 months or more to make, especially in cases wherein complex integrations and compliance testing are involved.
Portals apply a variety of cybersecurity applied by encryption, secure login protocols, audit trails, and role-based access control. They are also subjected to regulation, such as HIPAA-compliant cloud storage for healthcare professionals in the USA, ensuring the security and confidentiality of patients’ information.
Key features in a patient portal software include:
Advanced features might include telehealth, AI chat, and wearable integrations.
If you’re thinking about developing your own patient portal software, now’s the time to act. Let’s talk about how to bring your vision to life.